Choking can be a frightening experience, especially when it involves a child. Knowing how to respond quickly and effectively in such situations is crucial for ensuring the child’s safety. In this article, we will provide you with essential information on how to help a choking child. From understanding the causes and symptoms of choking to learning the proper first aid techniques, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to respond in times of emergency.
Accidents can happen at any time, and choking is one such incident that can occur unexpectedly. Children, particularly those under the age of five, are more susceptible to choking due to their natural curiosity and tendency to explore their surroundings with their mouths. Being aware of the appropriate steps to take when a child is choking can make a significant difference in their outcome.
Understanding choking in children
What is choking?
Choking occurs when an object or a piece of food becomes lodged in the throat or windpipe, blocking the airway and making it difficult to breathe. It is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate action.
Common causes of choking in children
Children can choke on a variety of objects, including small toys, coins, food, or even their own vomit. Common culprits include grapes, nuts, popcorn, hot dogs, and hard candies. It’s important to be aware of potential choking hazards to minimize the risk.
Signs and symptoms of choking
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of choking is crucial for prompt intervention. A choking child may exhibit the following indications:
- Difficulty breathing or noisy breathing
- Gasping for air
- Inability to speak or cry
- Clutching the throat or pointing to the throat
- Bluish discoloration of the lips or face
- Loss of consciousness (in severe cases)

When to call emergency services
If the child becomes unconscious or if the obstruction persists despite your efforts, call emergency services right away. Time is of the essence in such situations, and professional medical assistance may be required.
Recognizing and managing a partial airway obstruction
Signs and symptoms of a partial obstruction
Partial airway obstruction can be challenging to detect but requires prompt attention. Look out for the following signs:
- Mild difficulty breathing
- Coughing or wheezing
- Partially effective cough
Steps to take when a child is partially choking
- Encourage the child to cough to attempt to dislodge the object.
- Stay with the child and monitor their condition closely.
- If the obstruction worsens or the child shows signs of distress, seek medical help immediately.
Recognizing and managing a complete airway obstruction
Signs and symptoms of a complete obstruction
Complete airway obstruction is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention. Recognize the following signs:
- Inability to breathe or cough
- Panic or distress
- Cyanosis (bluish discolouration)
Steps to take when a child is completely choking
- Perform the Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrusts) immediately.
- Call emergency services if the child loses consciousness or if the obstruction persists.
Immediate response to a choking child
Assessing the severity of the situation
When encountering a choking child, it’s essential to assess the severity of the obstruction. Mild obstructions allow some airflow, while severe obstructions can completely block the airway. Understanding the level of obstruction will guide your next steps.
Performing first aid for choking
Step 1: Recognize the Signs
Be vigilant! Knowing the signs of a choking child is crucial. They may exhibit gasping, inability to speak, or clutching their throat.
Step 2: Stay Calm and Act Fast
Remember to stay calm in a choking emergency. Acting swiftly is essential. Seconds matter!
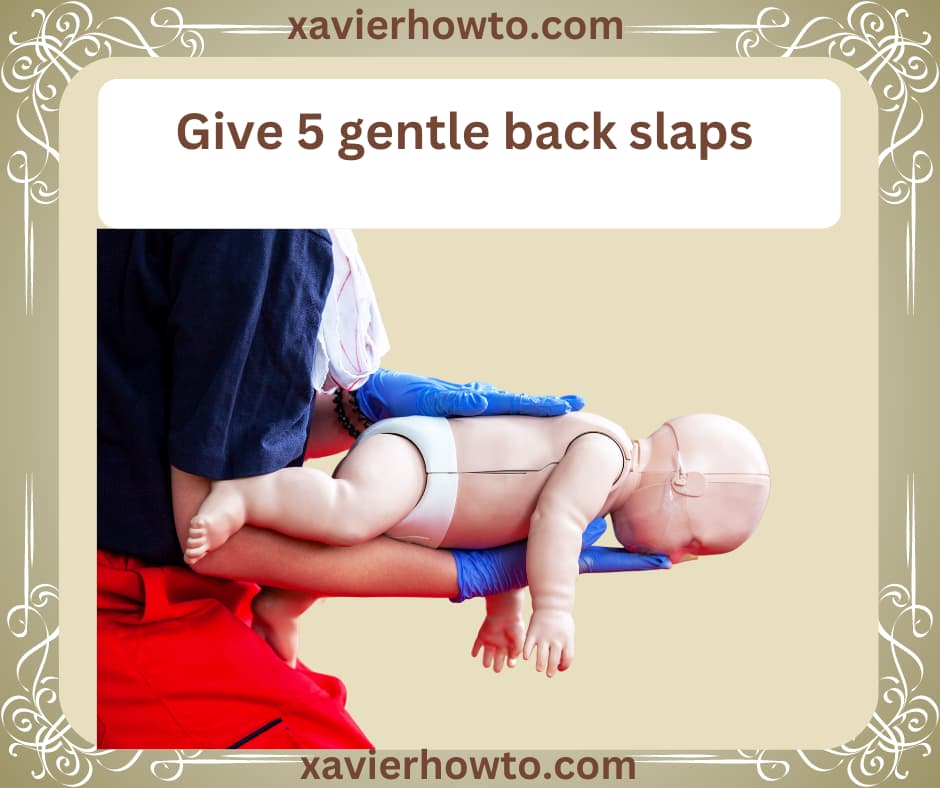
Step 3: Perform Back Blows
Deliver firm back blows to dislodge the object obstructing the airway. Bend the child forward and use the heel of your hand between the shoulder blades.
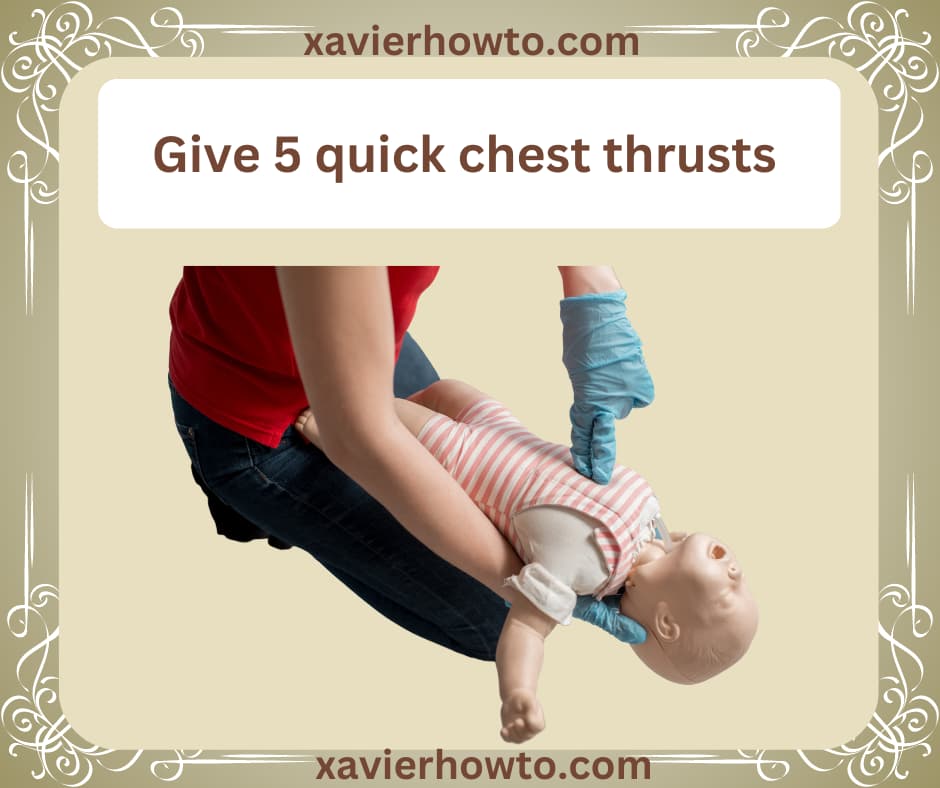
Step 4: Perform Chest Thrusts
If back blows do not work, move on to chest thrusts. Place your hand in the middle of the child’s chest and push inward and upward sharply.
Step 5: Call for Help
While performing first aid, remember to call for medical assistance or ask someone nearby to do it for you. Every second counts.
Step 6: Continue Cycles
Alternate between back blows and chest thrusts until the child starts breathing or help arrives. Stay persistent and determined
Common mistakes to avoid
In the heat of the moment, it’s easy to make mistakes that can worsen the situation. Avoid these common errors when helping a choking child:
Slapping the child on the back
While it may seem instinctive, slapping a choking child on the back can lodge the object further into the airway. This action should be avoided.
Using improper techniques
Using incorrect techniques, such as performing abdominal thrusts on infants or small children, can cause harm. Make sure to apply the appropriate methods based on the child’s age and size.
Delaying seeking medical help
If the obstruction does not resolve or the child’s condition deteriorates, do not delay seeking professional medical help. Emergency services are equipped to handle such situations.
Follow-up care and when to seek medical attention
After successfully resolving a choking incident, it’s important to provide appropriate follow-up care. Observe the child closely and look for signs that may indicate the need for further medical evaluation, including persistent coughing, wheezing, or difficulty swallowing. If any concerns arise, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Preventive measures
Preventing choking incidents is crucial for child safety. Consider implementing the following preventive measures:
1. Childproofing the environment
Childproofing your home is an effective way to minimize potential choking hazards. Keep small objects, coins, and batteries out of reach. Ensure electrical cords are secured, and use safety gates to restrict access to certain areas.
2. Safe eating habits
Teach children to sit down and eat slowly, avoiding talking or laughing with a mouthful of food. Cut food into small, manageable pieces, especially for young children. Avoid giving hard candies, popcorn, or other high-risk foods to young children.
3. Choosing age-appropriate toys
When selecting toys for children, ensure they are age-appropriate and do not pose a choking hazard. Avoid toys with small parts that can be easily detached or broken. Regularly inspect toys for any signs of wear or damage.
4. Basic first aid and CPR training
Obtaining basic first aid and CPR training equips you with essential life-saving skills. Enroll in a certified course to learn how to respond to emergencies effectively. Being prepared can make a significant difference in critical situations.
Conclusion
Knowing how to help a choking child is a critical skill for parents, caregivers, and anyone who spends time with children. By understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and implementing proper first aid techniques, you can provide immediate assistance when it matters most. Remember to childproof your environment, promote safe eating habits, and seek proper training in first aid and CPR. Being prepared can save lives and protect our little ones.
FAQs On How To Help A Choking Child
1. What are the most common choking hazards for children?
Children can choke on small toys, coins, food items such as grapes, nuts, popcorn, and hot dogs, as well as objects they put in their mouths. It’s important to be vigilant and keep these items out of reach.
2. How can I childproof my home to prevent choking incidents?
Childproofing your home involves securing small objects, coins, and batteries, using safety gates, and keeping electrical cords out of reach. Regularly inspect the environment for potential hazards.
3. Can I perform the Heimlich maneuver on an infant?
For infants younger than one year, perform back blows and chest thrusts instead of the Heimlich maneuver. It’s important to learn the appropriate techniques for each age group.
4. Is it necessary to call emergency services every time a child chokes?
If the child is able to cough and breathe, you can closely monitor them. However, if the obstruction worsens, the child loses consciousness, or the obstruction persists, call emergency services immediately.
5. How can I learn first aid and CPR for children?
Look for certified courses in your community that offer training in first aid and CPR specifically for infants and children. These courses provide valuable skills and knowledge in emergency situations.