Dysmenorrhea, commonly known as menstrual cramps, affects millions of women worldwide. It is a common condition characterized by painful menstrual periods, often accompanied by other symptoms such as bloating, fatigue, and mood swings. This menstrual disorder affects approximately 50-90% of menstruating women. If you are one of the many women struggling to manage dysmenorrhea, this article is for you. In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about managing menstrual Cramps including causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
CAUSES OF DYSMENORRHEA
Dysmenorrhea can have various causes, depending on the type of dysmenorrhea a person is experiencing. The most commonly identified causes of menstrual Cramps include :
- Prostaglandins: hormone-like substances that cause the uterus to contract and shed its lining during menstruation.
- Genetics: Some women may be more susceptible to Menstrual Cramps due to genetic factors.
- Age: Dysmenorrhea is more common in teenagers and women in their early twenties. This could be ascribed to the fact that the female reproductive hormones diminish as they age. Thus low uterine activity.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise may increase the risk of dysmenorrhea.
- Endometriosis: A condition in which the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of the uterus, causing pain and discomfort.
- Uterine fibroids: Non-malignant growths that develop in the uterus. These tumors can distort the normal structure of the uterus thus causing both cramps and menorrhagia during menstruation
- Adenomyosis: A condition in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows into the walls of the uterus. This condition causes bleeding into the uterine wall(wall of the uterus) hence pains due to stretch and contractions.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): An infection and inflammation of the reproductive organs.
- Cervical stenosis: A condition characterized by the narrowing of the cervix, Which makes it difficult for menstrual blood to pass through.
- Previous pelvic surgery: Scar tissue from previous surgeries can cause pain and discomfort during menstruation.
- Childbirth: Women who have given birth may experience more severe menstrual cramps.
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs): IUDs can cause heavier menstrual bleeding and more severe cramping in some women.
TYPES OF DYSMENORRHEA
Primary Dysmenorrhea
Primary dysmenorrhea is caused by the production of. The higher the level of prostaglandins in the body, the more severe the menstrual cramps can be. This type of Menstrual Cramps usually starts as early as during Menarche and is sometimes associated with one or more of the factors mentioned above.
Secondary Dysmenorrhea
Secondary dysmenorrhea is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). It often develops later in life and is more severe than primary dysmenorrhea.
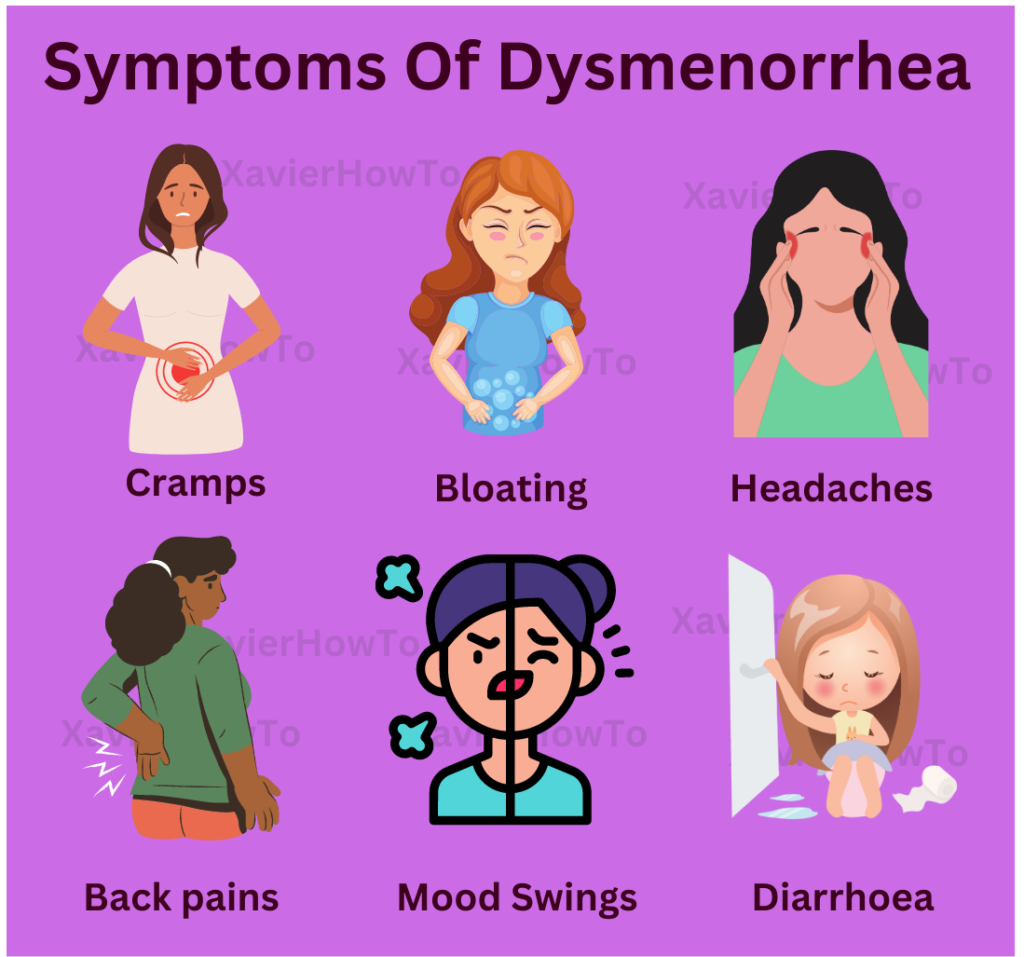
SYMPTOMS OF DYSMENORRHEA
The symptoms of Menstrual Cramps can vary from mild to severe, most often they are associated with the contractile movement of the myometrium during menstruation and can include:
- Cramping and pain in the lower abdomen
- Back pain
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Bloating
- Mood swings
Managing Dysmenorrhea
Managing Menstrual Cramps can involve a combination of lifestyle changes, over-the-counter pain relievers, and prescription medications.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage Menstrual Cramps symptoms. These changes include:
- Getting regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol
- Quitting smoking
- Applying heat to the lower abdomen
- Practicing relaxation techniques can help distract from the pain and discomfort. relaxation techniques include Yoga and meditation.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium, can help manage Menstrual Cramps symptoms. These medications work by reducing the production of prostaglandins, which can alleviate pain and cramping.
Prescription Medications
If over-the-counter pain relievers are not effective, your healthcare provider may recommend prescription medications, such as hormonal birth control or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal supplements, may also help manage Menstrual Cramps symptoms. However, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider before trying any alternative therapies.